|
Stevens's typology[edit]. Debate on Stevens's typology[edit]. Further. reading[edit]. Ordinal scaling[edit]. Other proposed typologies[edit]. Scale types and Stevens's "operational theory of. measurement"[edit]. Mathematical. operations[edit]. Central tendency[edit]. Central tendency[edit]. Central tendency and statistical. dispersion[edit]. Central tendency and statistical. dispersion[edit]. Mosteller and Tukey's typology (1977)[edit]. Chrisman's typology (1998)[edit]. Same variable may be different scale type depending on context[edit]. Show
Top 1: Level of measurement - WikipediaAuthor: en.wikipedia.org - 82 Rating
Description: Stevens's typology[edit]. Debate on Stevens's typology[edit]. Further. reading[edit]. Ordinal scaling[edit]. Other proposed typologies[edit]. Scale types and Stevens's "operational theory of. measurement"[edit]. Mathematical. operations[edit]. Central tendency[edit]. Central tendency[edit]. Central tendency and statistical. dispersion[edit]. Central tendency and statistical. dispersion[edit]. Mosteller and Tukey's typology (1977)[edit]. Chrisman's typology (1998)[edit]. Same variable may be different scale type depending on context[edit].
Matching search results: Level of measurement or scale of measure is a classification that describes the nature of information within the values assigned to variables. Psychologist Stanley Smith Stevens developed the best-known classification with four levels, or scales, of measurement: nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio. This framework of distinguishing levels of measurement originated … ...
Top 2: Levels of Measurement | Nominal, Ordinal, Interval and RatioAuthor: scribbr.com - 117 Rating
Description: Nominal, ordinal,. interval, and ratio data. Why are levels of measurement important?. Which descriptive statistics can I apply on my data?. Quiz: Nominal, ordinal, interval, or ratio?. Frequently asked questions about levels of. measurement. Cite this Scribbr article. Is this article helpful? Published on July 16, 2020 by Pritha Bhandari. Revised on December 5, 2022. Levels of measurement, also called scales of measurement, tell you how precisely. variables are recorded. In scientific research,
Matching search results: Jul 16, 2020 · Example of a variable at 2 levels of measurement You can measure the variable of income at an ordinal or ratio level. Ordinal level: You create brackets of income ranges: $0–$19,999, $20,000–$39,999, and $40,000–$59,999. You ask participants to select the bracket that represents their annual income. ...
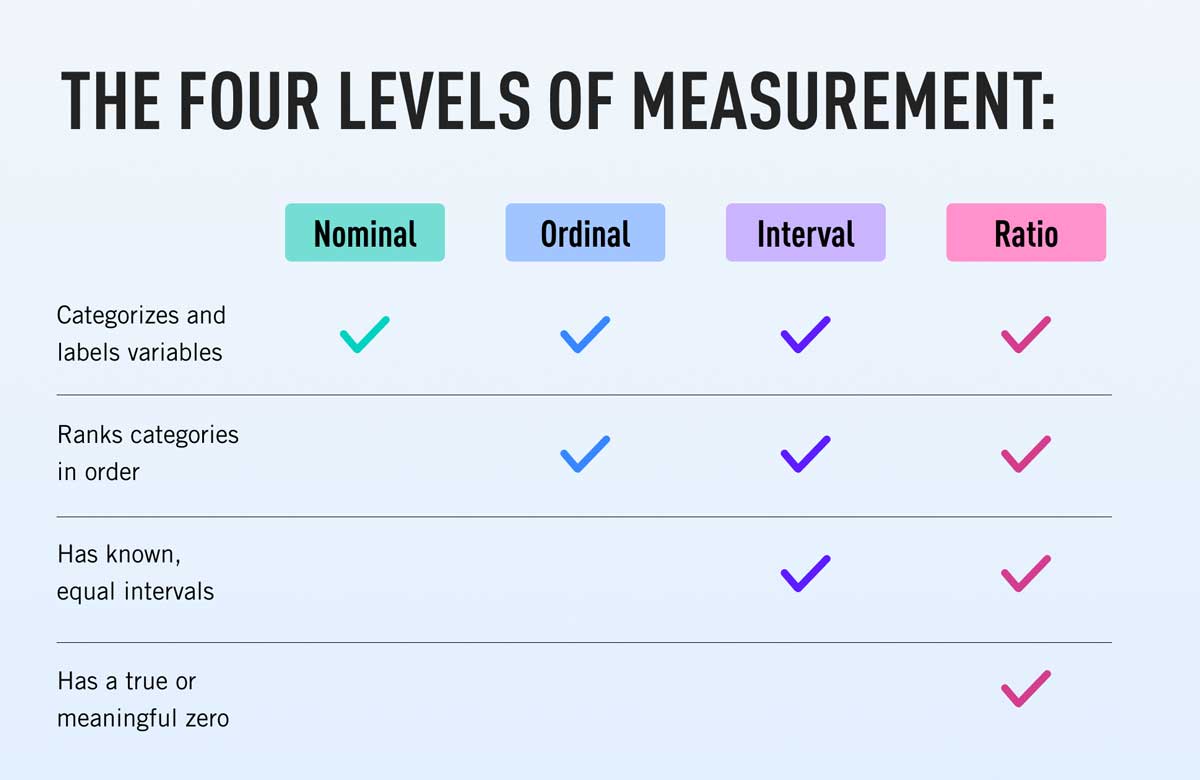 Top 3: 4 Levels of Measurement: Nominal, Ordinal, Interval & RatioAuthor: careerfoundry.com - 135 Rating
Description: 1. What are levels of measurement in data and statistics?. 2. Why are levels of measurement important?. 3. What are the four levels of measurement? Nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio scales explained. What is the nominal level?. Examples of nominal data. How to analyze nominal data. What is the. ordinal level?. Examples of ordinal data. How to analyze ordinal data. What is the interval level?. Examples of interval data. How to analyze interval data. What is the ratio level?. Examples of ratio data. How to analyze ratio data. 1.. Descriptive statistics for nominal data. 2. Statistical tests for analyzing nominal data. 1. Descriptive statistics for ordinal data. 2. Statistical tests for analyzing ordinal data. 1. Descriptive statistics for interval data. 2. Statistical tests for analyzing interval data. 1.. Descriptive statistics for ratio data. 2. Statistical tests for analyzing ratio data.
Matching search results: Nov 30, 2022 · An oft-cited example of interval data is temperature in Fahrenheit, where the difference between 10 and 20 degrees Fahrenheit is exactly the same as the difference between, say, 50 and 60 degrees Fahrenheit. Learn more about interval data in this guide. ... (the fourth level of measurement), interval data has no true zero; in other words, a ... ...
Top 4: Levels of Measurement: Nominal, Ordinal, Interval, and Ratio ScalesAuthor: kyleads.com - 134 Rating
Description: What are the nominal, ordinal, interval, ratio scales really?. Example of nominal scales. Ordinal scale examples. Nominal scale vs ordinal scale. Example of an interval scale. Example of ratio scale question. Interval scale vs ratio scale When you’re collecting qualitative and quantitative data through different types of surveys and research instruments 4 data measurement scales are often used. They’re referred to as nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio scales.Each of the measurement scales bu
Matching search results: Feb 13, 2020 · The interval scale is the third level of measurement and encompasses both nominal and ordinal scales. ... For example, credit score is an interval scale but it starts at 300. With that being said, every point on the scale is equidistant from the next. On a Celsius scale, each unit is the same size or has the same value. We can, without a doubt ... ...
 Top 5: Standard deviation - WikipediaAuthor: en.wikipedia.org - 78 Rating
Description: Definition of population values[edit]. Identities and mathematical properties[edit]. Interpretation and. application[edit]. Relationship between standard deviation and mean[edit]. Rapid calculation methods[edit]. Higher dimensions[edit]. Population standard deviation of grades of eight students[edit]. Standard deviation of average height for adult men[edit]. Discrete random variable[edit]. Continuous random. variable[edit]. Uncorrected sample standard deviation[edit]. Corrected sample standard deviation[edit]. Unbiased sample standard. deviation[edit]. Confidence interval of a sampled standard deviation[edit]. Bounds on standard. deviation[edit]. Application examples[edit]. Geometric. interpretation[edit]. Chebyshev's inequality[edit]. Rules for normally distributed data[edit]. Standard deviation of the mean[edit]. Weighted. calculation[edit]. Experiment, industrial and hypothesis. testing[edit].
Matching search results: In statistics, the standard deviation is a measure of the amount of variation or dispersion of a set of values. A low standard deviation indicates that the values tend to be close to the mean (also called the expected value) of the set, while a high standard deviation indicates that the values are spread out over a wider range.. Standard deviation may be abbreviated SD, and is most … ...
 Top 6: Sample Size Calculator - Confidence Level, Confidence Interval, …Author: surveysystem.com - 106 Rating
Description: Sample Size Calculator Terms: Confidence Interval & Confidence Level. Factors that Affect Confidence Intervals This Sample Size Calculator is presented as a public service of Creative Research Systems survey software. You can use it to determine how many people you need to interview in order to get results that reflect the target population as precisely as needed. You can also find the level of precision you have in. an existing sample.Before using the sample size calculator, there are two terms
Matching search results: Sample Size Calculator Terms: Confidence Interval & Confidence Level. The confidence interval (also called margin of error) is the plus-or-minus figure usually reported in newspaper or television opinion poll results. For example, if you use a confidence interval of 4 and 47% percent of your sample picks an answer you can be "sure" that if you had asked the question of … ...
 Top 7: Understanding Confidence Intervals | Easy Examples & Formulas …Author: scribbr.com - 120 Rating
Description: What exactly is a confidence interval?. Calculating a. confidence interval: what you need to know. Confidence interval for the mean of normally-distributed data. Confidence interval for proportions. Confidence interval for non-normally distributed data. Reporting. confidence intervals. Caution when using confidence intervals. Frequently asked questions about confidence intervals. When do you use confidence intervals?. Finding the critical value. Finding the standard deviation. What can proofreading do for your paper?. Cite this Scribbr article. Is this article helpful?.
Matching search results: Aug 07, 2020 · For example, if you construct a confidence interval with a 95% confidence level, you are confident that 95 out of 100 times the estimate will fall between the upper and lower values specified by the confidence interval. Your desired confidence level is usually one minus the alpha (α) value you used in your statistical test: Confidence level ... ...
 Top 8: Unbanked American households hit record low numbers in 2021Author: usatoday.com - 152 Rating
Description: What does it mean to be unbanked?. Who are the underbanked?. Why are people unbanked or underbanked?. Are some groups more likely to be unbanked? . Will the number of unbanked rise if the U.S. has a recession? The number of American households that were unbanked last year dropped to its lowest level since 2009, a dip due in part to people opening accounts to receive financial assistance during the pandemic, a new report says. Roughly 4.5% of U.S. households – or 5.9 million&nbs
Matching search results: Oct 25, 2022 · The number of American households that were unbanked last year dropped to its lowest level since 2009, a dip due in part to people opening accounts to receive financial assistance during the ... ...
 Top 9: Force - WikipediaAuthor: en.wikipedia.org - 52 Rating
Description: Development of the concept[edit]. Pre-Newtonian. concepts[edit]. Newtonian. mechanics[edit]. Special theory of. relativity[edit]. Fundamental. forces[edit]. Non-fundamental forces[edit]. Rotations and torque[edit]. Kinematic. integrals[edit]. Potential. energy[edit]. Units of. measurement[edit]. Force measurement[edit]. Further reading[edit]. Forces in quantum. mechanics[edit]. Feynman. diagrams[edit]. Electromagnetic[edit]. Continuum. mechanics[edit]. Fictitious forces[edit]. Centripetal force[edit]. Conservative. forces[edit]. Nonconservative. forces[edit].
Matching search results: For example, an object on a level surface is pulled (attracted) downward toward the center of the Earth by the force of gravity. ... and has a magnitude of about 9.81 meters per second squared (this measurement is taken from sea level and may vary depending on location), and points toward the center of the Earth. ... in a time interval dt:: ... ...
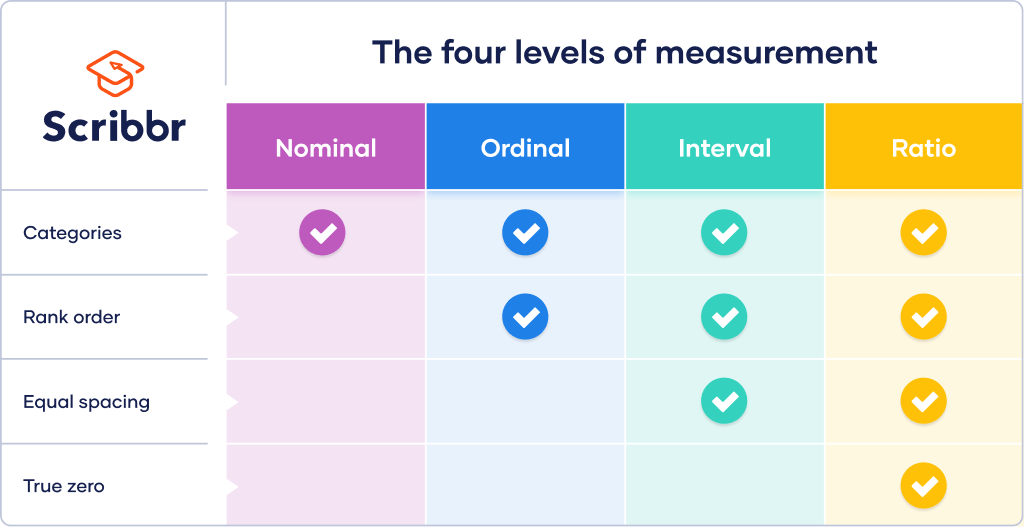 Top 10: Ratio Scales | Definition, Examples, & Data Analysis - ScribbrAuthor: scribbr.com - 108 Rating
Description: Levels of measurement. Examples of ratio scales. Frequently asked questions about ratio data. Cite this Scribbr article. Is this article helpful? Published on August 28, 2020 by Pritha Bhandari. Revised on November 28, 2022. A ratio scale is a quantitative scale where there is a true zero and equal intervals between neighboring points. Unlike on an interval scale, a zero on a ratio scale means there is a total absence of. the variable you are measuring.Length, area, and population are examples
Matching search results: Aug 28, 2020 · The levels, or scales, of measurement indicate how precisely data is recorded. The higher the level, the more complex the measurement is. The ratio level contains all of the features of the other 3 levels. At the ratio level, values can be categorized, ordered, have equal intervals and take on a true zero. ...
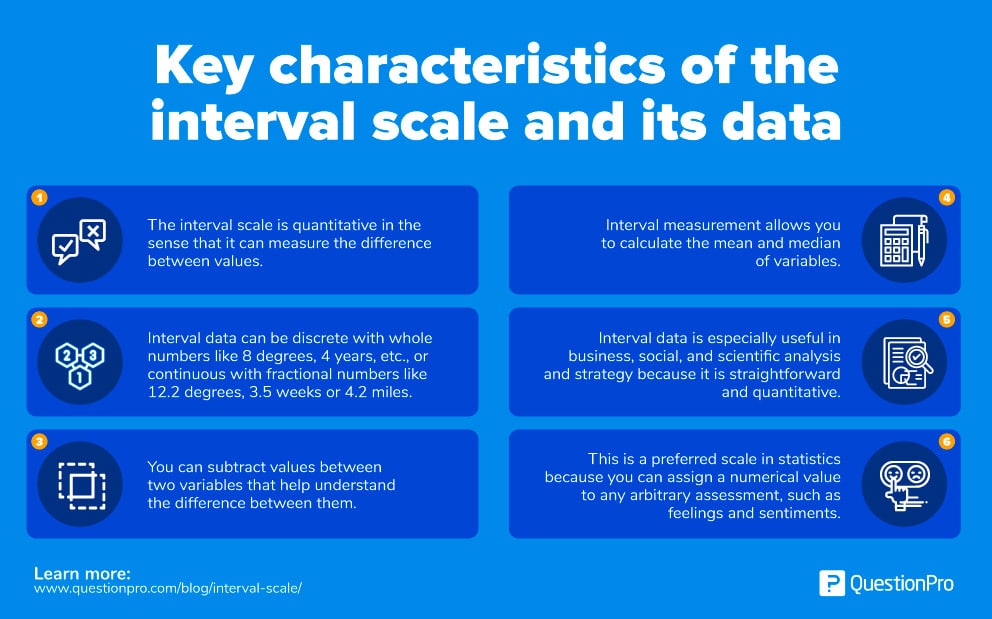 Top 11: Interval Scale: Definition, Characteristics with Examples | QuestionProAuthor: questionpro.com - 119 Rating
Description: Characteristics of interval scale. Interval scale examples. Net Promoter Score (NPS) As you create a plan for analyzing quantitative data from your surveys, chances are you’ve come across the phrase “interval scale.” But what is the it, and how does it differ from commonly associated terms like “nominal scale” and “ordinal scale”?We’ll cover the definition, describe key characteristics, and provide interval scale examples that could be especially useful for your survey strategy.The interval sca
Matching search results: The interval scale is defined as the 3rd quantitative level of measurement where the difference between 2 variables is meaningful.The interval scale is defined as the 3rd quantitative level of measurement where the difference between 2 variables is meaningful. ...
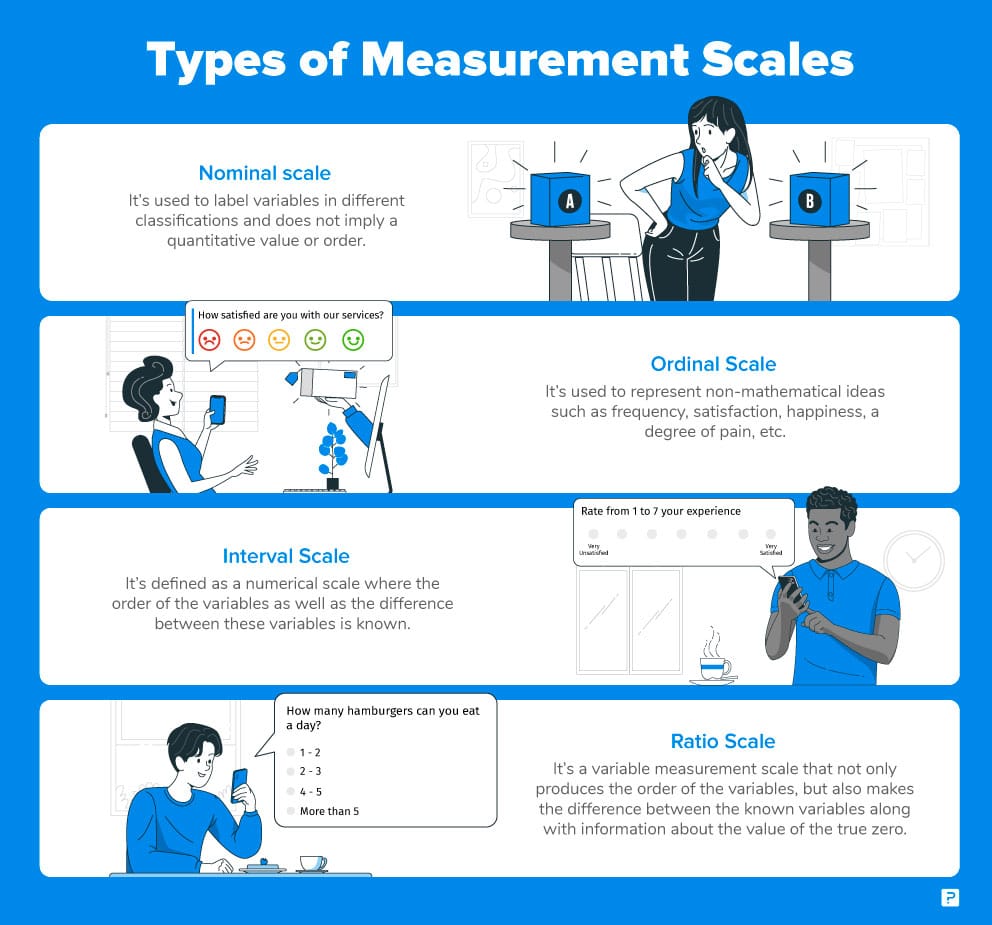 Top 12: Nominal, Ordinal, Interval, Ratio Scales with Examples - QuestionProAuthor: questionpro.com - 132 Rating
Description: Levels of Measurement in Statistics. Ordinal Scale: 2nd Level of Measurement. Interval Scale: 3rd Level of Measurement. Ratio Scale: 4th Level of Measurement. Summary – Levels of Measurement. Nominal Scale Data and Analysis. Nominal Scale Examples. Ordinal Data and Analysis . Ordinal Scale Examples. Interval Data and Analysis. Interval Scale Examples. Ratio Data and Analysis. Ratio Scale Examples Levels of Measurement in StatisticsTo perform statistical analysis of data, it is important to
Matching search results: Nominal, Ordinal, Interval and Ratio are the four fundamental levels of measurement scales used to capture data using surveys and questionnaires.Interval Scale Vs Ratio Scale · Nominal vs Ordinal Scale · Bipolar Matrix TableNominal, Ordinal, Interval and Ratio are the four fundamental levels of measurement scales used to capture data using surveys and questionnaires.Interval Scale Vs Ratio Scale · Nominal vs Ordinal Scale · Bipolar Matrix Table ...
 Top 13: 10 Interval Data Examples: Interval Scale Definition & MeaningAuthor: intellspot.com - 112 Rating
Description: In the world of data management, statistics or marketing research, there are so many things you can do with interval data and the interval scale. With this in mind, there are a lot of interval data examples that can be given. In fact, together with ratio data, interval data is the basis of the power that statistical analysis can show. Both interval and ratio scales represent the highest level of data measurement and help a. wide range of statistical manipulations and transform
Matching search results: Interval Scale Examples, Definition and Meaning · 1. Time of each day in the meaning of a 12-hour clock. · 2. Temperature, in degrees Fahrenheit or Celsius (but ...Interval Scale Examples, Definition and Meaning · 1. Time of each day in the meaning of a 12-hour clock. · 2. Temperature, in degrees Fahrenheit or Celsius (but ... ...
 Top 14: 4 Levels of Measurement: Nominal, Ordinal, Interval & RatioAuthor: careerfoundry.com - 135 Rating
Description: 1. What are levels of measurement in data and statistics?. 2. Why are levels of measurement important?. 3. What are the four levels of measurement? Nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio scales explained. What is the nominal level?. Examples of nominal data. How to analyze nominal data. What is the. ordinal level?. Examples of ordinal data. How to analyze ordinal data. What is the interval level?. Examples of interval data. How to analyze interval data. What is the ratio level?. Examples of ratio data. How to analyze ratio data. 1.. Descriptive statistics for nominal data. 2. Statistical tests for analyzing nominal data. 1. Descriptive statistics for ordinal data. 2. Statistical tests for analyzing ordinal data. 1. Descriptive statistics for interval data. 2. Statistical tests for analyzing interval data. 1.. Descriptive statistics for ratio data. 2. Statistical tests for analyzing ratio data.
Matching search results: Nov 30, 2022 · The interval level is a numerical level of measurement which, like the ordinal scale, places variables in order. Unlike the ordinal scale, ...What are levels of... · What are the four levels of... · Nominal level · Ordinal levelNov 30, 2022 · The interval level is a numerical level of measurement which, like the ordinal scale, places variables in order. Unlike the ordinal scale, ...What are levels of... · What are the four levels of... · Nominal level · Ordinal level ...
 Top 15: What Is Interval Data? [Definition, Analysis & Examples]Author: careerfoundry.com - 127 Rating
Description: 1. An introduction to the four different types of. data. 3. What are some examples of interval data?. 4. How is. interval data collected and what is it used for?. 5. How to analyze interval data. 6. Summary and further reading. Why do the different levels of measurement matter?. Key characteristics of. interval data. What’s the difference between interval data and ratio data?. How is interval data used?. Descriptive statistics for interval data. Inferential statistics for interval data. Frequency distribution. Measures of central tendency: Mode, median, mean. Measures of variability: Range, standard deviation, and variance. Pearson correlation coefficient. Simple linear regression.
Matching search results: Aug 20, 2021 · Temperature in Fahrenheit or Celsius (-20, -10, 0, +10, +20, etc.) · Times of the day (1pm, 2pm, 3pm, 4pm, etc.) · Income level on a continuous ...Aug 20, 2021 · Temperature in Fahrenheit or Celsius (-20, -10, 0, +10, +20, etc.) · Times of the day (1pm, 2pm, 3pm, 4pm, etc.) · Income level on a continuous ... ...
 Top 16: Level of Measurement - Overview, Types of Scales, ExamplesAuthor: corporatefinanceinstitute.com - 140 Rating
Description: What is Level of Measurement?. Four Measurement Levels A classification that relates the values that are assigned to variables with each otherWhat is Level of Measurement?In statistics, level of measurement is a classification that relates the values that are assigned to variables with each other. In other words, level of measurement is used to describe information within the values. Psychologist Stanley Smith is known for developing four levels of measurement: nominal, ordinal, interval, and r
Matching search results: Nov 28, 2022 · For example, temperature measurement is an example of an interval scale: 60°C is colder than 65°C, and the temperature difference is the ...Nov 28, 2022 · For example, temperature measurement is an example of an interval scale: 60°C is colder than 65°C, and the temperature difference is the ... ...
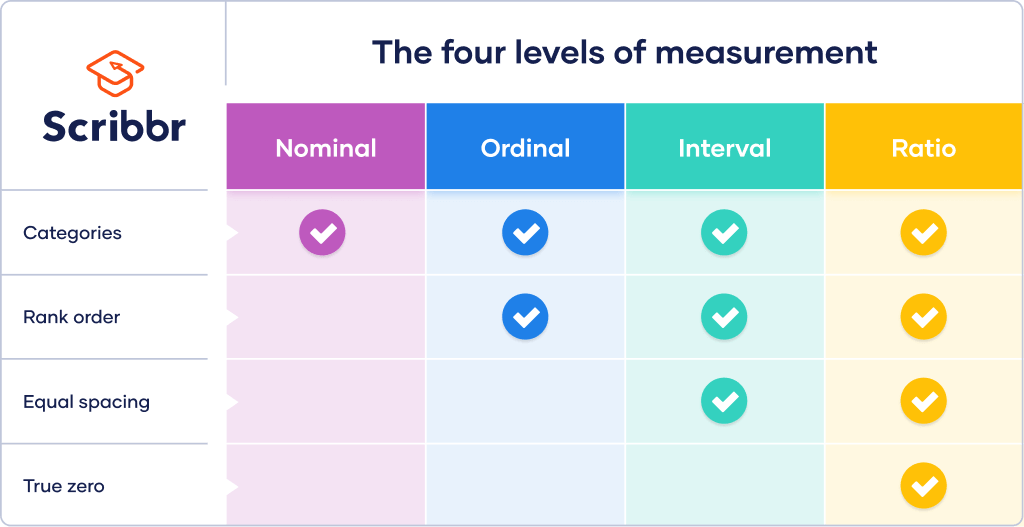 Top 17: Interval Data and How to Analyze It | Definitions & Examples - ScribbrAuthor: scribbr.com - 119 Rating
Description: Levels. of measurement. Interval vs ratio scales. Examples of interval data. Interval data analysis. Frequently asked questions about interval data. Receive feedback on language, structure and formatting. Cite this Scribbr article. Is this article helpful? Published on August 28, 2020 by Pritha Bhandari. Revised on November 17, 2022. Interval data is measured along a numerical scale that has equal distances between adjacent values. These distances are called “intervals.”There is no true zero o
Matching search results: Aug 28, 2020 · Celsius and Fahrenheit are examples of interval scales. Each point on these scales differs from neighboring points by intervals of exactly one ...Aug 28, 2020 · Celsius and Fahrenheit are examples of interval scales. Each point on these scales differs from neighboring points by intervals of exactly one ... ...
 Top 18: Levels of Measurement - Research Methods Knowledge BaseAuthor: conjointly.com - 103 Rating
Description: Why is Level of Measurement Important? The level of measurement refers to the relationship among the values that are assigned to the attributes for a variable. What does that mean? Begin with the idea of the variable, in this example “party affiliation.”That variable has a number of attributes. Let’s assume that in this particular election context the only. relevant attributes are “republican”, “democrat”, and “independent”. For purposes of analyzing the results of this variable, we arbitrarily
Matching search results: In interval measurement the distance between attributes does have meaning. For example, when we measure temperature (in Fahrenheit), the distance from 30-40 is ...In interval measurement the distance between attributes does have meaning. For example, when we measure temperature (in Fahrenheit), the distance from 30-40 is ... ...
|

Related Posts
Advertising
LATEST NEWS
Advertising
Populer
Advertising
About

Copyright © 2024 ihoctot Inc.


















